Archive Note: Embedded capacitor technology is used in production for specialized applications, but the supplier base remains limited. High-Dk materials from companies like DuPont and Oak-Mitsui exist, but not all PCB manufacturers have qualified processes. This article explains the technology for educational purposes.
The Problem: Discrete Capacitors Consume Board Space
Surface-mount capacitors take up valuable real estate on crowded boards. In high-density designs, especially under BGAs where you need local decoupling, there’s often no room for the dozens of capacitors required.
Embedded capacitors solve this by forming capacitance within the PCB layers themselves, freeing surface area for active components.
How Embedded Capacitors Work
A capacitor is simply two conductors separated by a dielectric. In a PCB, you can form capacitors using:
- Thin dielectric layers (12–25 µm) between copper planes
- High-Dk materials that provide more capacitance per unit area
- Defined copper pads on adjacent layers
The capacitance formula: C = ε₀ × εᵣ × A / t
Where:
- C = Capacitance (Farads)
- ε₀ = Permittivity of free space (8.85 × 10⁻¹² F/m)
- εᵣ = Dielectric constant of the material
- A = Overlap area of the conductors
- t = Dielectric thickness
Because capacitance scales with area and inversely with thickness, embedded capacitors are best suited for smaller values, typically picofarads to low nanofarads.
Materials
Several manufacturers offer high-Dk laminates specifically designed for embedded capacitance:
| Material | Manufacturer | Dk | Typical Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| BC2000 | Hadco/Sanmina | ~17 | 4–12 µm |
| Interra HK | DuPont | ~10–20 | 4–24 µm |
| C-Ply | 3M (discontinued) | ~16 | 8–16 µm |
| FaradFlex | Oak-Mitsui | ~10–35 | 12–24 µm |
| Supplier | Sanmina | Sanmina | 3M | DuPont |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trade name | EmCap | BC2000 | C-Ply | HiK |
| Dielectric material | Epoxy Resin/Barium Titanate | FR-4 | Epoxy Resin/Barium Titanate | Polyimide core |
| Thickness µm | 100 | 50 | 25 | 25 |
| Capacitance Range nF/in² | 2.1 | 0.5 | 3.0 | 1.5 |
| Dissipation Factor tan δ 1GHz | 0.06 | 0.021 | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| Dielectric Constant εᵣ 1GHz | 36 | 3.9 | 22 | 11.6 |
Capacitance material comparison: higher Dk and thinner dielectric = more capacitance per area
Advantages
High-Frequency Performance
Surface-mount capacitors become ineffective above 1 GHz due to parasitic inductance. Embedded capacitors have virtually no lead inductance, providing effective decoupling into the GHz range.
Reduced Component Count
Each embedded capacitor eliminates a surface-mount part, reducing assembly cost and potential failure points.
Improved Reliability
No solder joints means no solder fatigue failures. The capacitor is integral to the PCB structure.
Lower Impedance
The distributed nature of embedded capacitance provides lower ESL (equivalent series inductance) than discrete components.
Applications
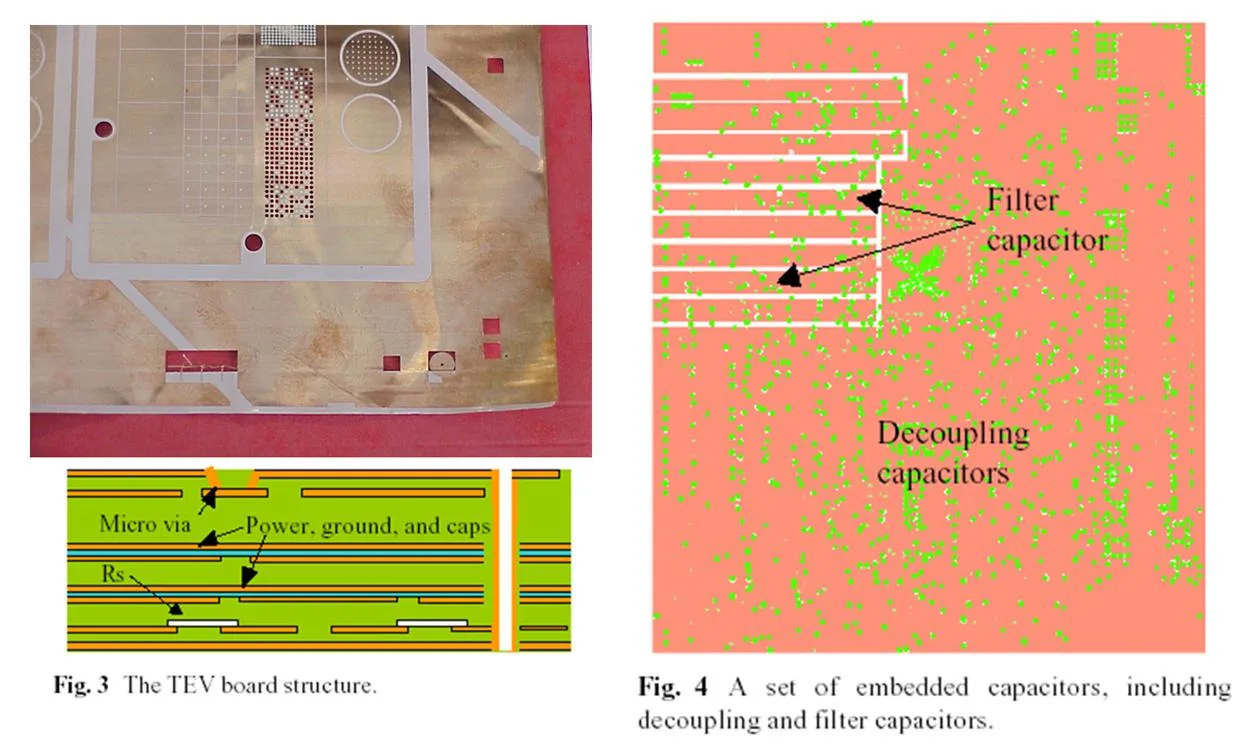
TEV board structure: embedded capacitors provide local decoupling without consuming surface area
Power Integrity
Embedded capacitors work well for mid-frequency decoupling (10 MHz – 1 GHz), complementing bulk capacitors at low frequencies and embedded capacitance layers at high frequencies.
Filter Networks
RC and LC filters can be implemented with embedded capacitors and embedded resistors.
Sensor Applications
Stable, well-characterised capacitors can serve as reference elements in capacitive sensing circuits.
Limitations
- Maximum capacitance is limited by available board area
- Tolerance is typically ±20% without trimming
- Cannot be replaced after lamination, so design verification is critical
- Cost premium for high-Dk materials and additional processing
When to Use Embedded Capacitors
This technology makes sense when:
- Board space is at a premium and decoupling is required under BGAs
- High-frequency decoupling (>500 MHz) is needed
- Long-term reliability is critical and solder joint failures are a concern
- The design is mature and capacitor values won’t change
For distributed power plane capacitance (effective at very high frequencies), see Embedded Capacitance Layers.
Industry Status
Embedded capacitor technology using high-Dk materials exists but has limited adoption outside specialized applications. The challenges include:
- Material availability - some products (like 3M C-Ply) have been discontinued
- Supplier qualification - few PCB manufacturers have production experience
- Design complexity - requires careful stackup planning and thermal analysis
- Cost justification - discrete capacitors are cheap and well-understood
Military, aerospace, and high-reliability applications use embedded capacitors where the benefits justify the complexity.
Related Articles
- Embedded Capacitance Layers - Power plane configurations with built-in capacitance
- Embedded Resistors in PCBs - Resistor embedding using Ohmega-Ply
- PCB Materials and Laminates Guide - Dielectric material specifications
Questions?
If you’re evaluating embedded capacitors for a specific application, contact us. We can discuss the technology and help you understand whether it makes sense for your requirements.