AC coupling
Design ConsiderationsUsing capacitors to pass AC signals while blocking DC between circuits.
View full definition
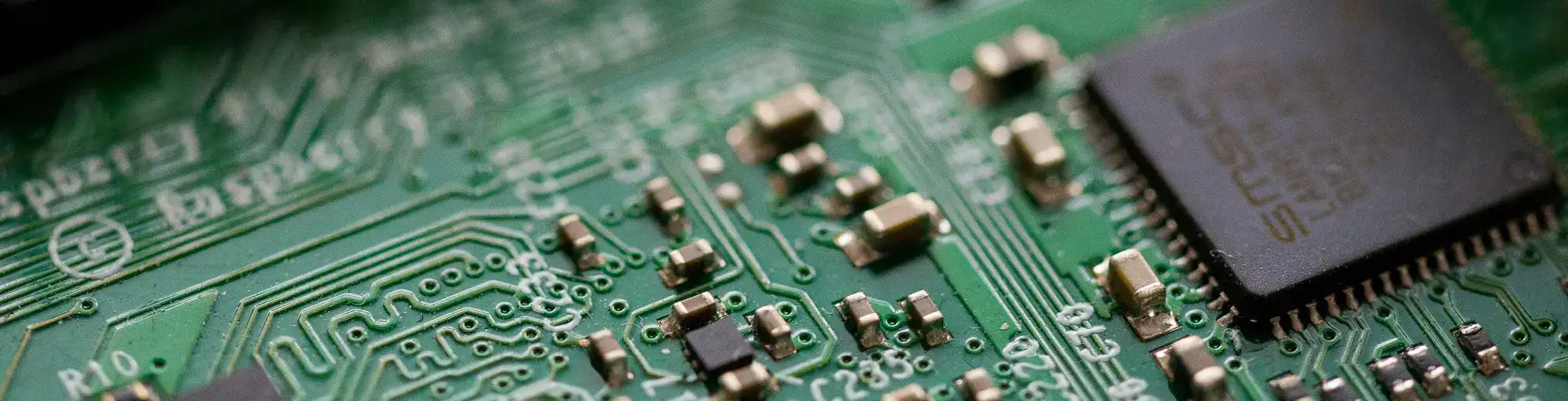
PCB manufacturing has its own language. This glossary covers 269 terms commonly used in printed circuit board design, fabrication, and assembly - from basic acronyms to advanced manufacturing processes.
Each term includes a brief definition for quick reference and a detailed explanation for deeper understanding. Terms link to related technical articles where available.
Using capacitors to pass AC signals while blocking DC between circuits.
View full definitionAutomotive stress test qualification for integrated circuits, with temperature grading from -50°C to +150°C.
View full definitionAutomotive stress test qualification for passive components including resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
View full definitionThe copper pad area surrounding a drilled hole, critical for reliable connections.
View full definitionPCB structure that radiates or receives electromagnetic energy.
View full definitionHDI technology where all layers can interconnect with micro-vias, without traditional through-holes.
View full definitionMachine vision system that inspects PCBs for defects by comparing images against reference designs.
View full definitionAerospace standard for counterfeit electronic parts avoidance, detection, and mitigation.
View full definitionAerospace quality management standard required by FAA, DoD, NASA, and major aerospace OEMs.
View full definitionRatio of hole depth to diameter, affecting plating quality in through-holes and vias.
View full definitionIsola's thermoset alternative to PTFE for automotive radar at 77 GHz.
View full definitionRemoving unused via stub portions to reduce signal integrity issues at high frequencies.
View full definitionFracture in via plating wall caused by thermal cycling stress.
View full definitionMinimum curve radius for flex circuits without damaging conductors or base material.
View full definitionSurface-mount package with solder balls arranged in a grid pattern on the underside.
View full definitionProcess of removing old solder balls from a BGA and attaching new ones for reuse or repair.
View full definitionVia connecting an outer layer to one or more inner layers without going through the entire board.
View full definitionTest methodology using on-chip logic to verify connections without physical probe access.
View full definitionPCB flatness deviations measured as warpage, critical for surface-mount assembly.
View full definitionDifferential traces stacked vertically on adjacent layers rather than side-by-side.
View full definitionHigh-performance laminate material with excellent thermal stability and low dielectric constant.
View full definitionProcess of adding layers to a core through sequential lamination in HDI fabrication.
View full definitionVia connecting inner layers without reaching either outer surface.
View full definitionSoftware for designing PCB layouts, schematics, and generating manufacturing files.
View full definitionElectrochemical failure mode where copper filaments grow along glass fibers.
View full definitionSoftware that converts PCB design data into manufacturing instructions.
View full definitionHalf-holes at PCB edges that form solderable connections for module attachment.
View full definitionBase material for PCB fabrication - laminate with copper foil bonded to one or both sides.
View full definitionInorganic substrate material offering superior thermal and electrical properties for demanding applications.
View full definitionThe impedance a transmission line presents to a signal, determined by geometry and materials.
View full definitionMinimum spacing between conductive features, determined by voltage and manufacturing limits.
View full definitionSurface microstrip covered with solder mask, lowering impedance by 2-3 ohms.
View full definitionSignal component present equally on both lines of a differential pair.
View full definitionMeeting regulatory and industry standard requirements for electronics.
View full definitionRegulations requiring disclosure of tin, tantalum, tungsten, and gold (3TG) sourcing from conflict regions.
View full definitionThin protective film applied to assembled PCBs to shield against environmental hazards.
View full definitionPCB traces designed and manufactured to a specific impedance value with tolerance.
View full definitionTransmission line with signal trace flanked by ground on the same layer.
View full definitionElectrochemical deposition of copper to build up trace thickness and plate hole walls.
View full definitionLarge area of copper filling unused space on a PCB layer, typically connected to ground or power.
View full definitionCopper thickness specified as weight per square foot, where 1 oz = 35 µm (1.4 mil).
View full definitionRigid laminate with copper on both sides, the structural building block of multilayer PCBs.
View full definitionFlexible polyimide film laminated over flex circuit traces instead of solder mask.
View full definitionShortest distance between conductors measured along the insulating surface, not through air.
View full definitionMesh pattern ground plane used in flex circuits to improve flexibility.
View full definitionUnwanted coupling of signals between adjacent traces.
View full definitionIC package where the package size is no more than 1.2x the die size.
View full definitionRate at which a material expands when heated, measured in ppm/°C.
View full definitionMaximum current a trace can carry without excessive temperature rise.
View full definitionProviding local energy storage to supply transient current demands from ICs.
View full definitionProcess of separating individual PCBs from a manufacturing panel after assembly.
View full definitionManufacturing constraints encoded in CAD tools to ensure producible designs.
View full definitionMeasure of signal energy lost as heat in a dielectric material, also called loss tangent.
View full definitionDesign practices that ensure a PCB can be manufactured reliably and cost-effectively.
View full definitionElectrically insulating material between conductive layers in a PCB.
View full definitionGround-signal-signal-ground configuration combining differential and coplanar benefits.
View full definitionImpedance seen between the two traces of a differential pair, approximately 2x odd-mode.
View full definitionTwo traces carrying complementary signals, providing noise immunity for high-speed signals.
View full definitionMeasure of a material's ability to store electrical energy, affecting signal speed and impedance.
View full definitionAutomated verification that a PCB design meets manufacturing constraints.
View full definitionCreating holes in PCBs mechanically or with lasers for vias and through-holes.
View full definitionTwo signal layers between outer ground planes, typically routed orthogonally.
View full definitionMajor supplier of specialty PCB materials including Pyralux flex materials and Interra high-Dk laminates.
View full definitionCopper plating on PCB edges for grounding, shielding, or electrical contact.
View full definitionTwo traces side-by-side on same layer with controlled gap spacing.
View full definitionChemical deposition of metal without external electrical current, for uniform coverage.
View full definitionMetal deposition using electric current, building up copper thickness on PCB features.
View full definitionCapacitance created in PCB inner layers using high-Dk dielectric materials.
View full definitionPassive or active device fabricated or placed within PCB inner layers.
View full definitionTrace buried in dielectric with single reference plane below, not between two planes.
View full definitionResistor fabricated directly into PCB inner layers using resistive foil or paste.
View full definitionAbility of equipment to function without causing or being affected by EMI.
View full definitionUnwanted electromagnetic energy that can disturb electronic equipment operation.
View full definitionThree-layer surface finish adding palladium for improved wire bonding and corrosion resistance.
View full definitionSurface finish with nickel barrier and thin gold layer, providing flat pads and good shelf life.
View full definitionRouting signals out from under BGA and CSP components to reach vias or traces.
View full definitionStandard for establishing ESD control programs protecting sensitive electronics during handling.
View full definitionChemical removal of unwanted copper to define traces and features.
View full definitionImpedance seen by each trace in a coupled pair when driven with identical signals.
View full definitionRouting from component pads to vias that connect to other layers.
View full definitionHigh-capacitance laminate material for embedded capacitance layers.
View full definitionInductive component that absorbs high-frequency noise while passing DC and low frequencies.
View full definitionImpedance variation caused by periodic glass/resin structure in PCB laminates.
View full definitionReference mark on a PCB used by pick-and-place machines for alignment.
View full definitionPCB built on flexible polyimide substrate that can bend and flex.
View full definitionDie mounting with the active side facing down, connected via solder bumps.
View full definitionChemical agent that cleans surfaces and promotes solder wetting during soldering.
View full definitionElectrical test method using moving probes for prototype and low-volume testing.
View full definitionThe copper pad pattern on a PCB that matches a component's physical package.
View full definitionStandard glass-reinforced epoxy laminate used in most PCBs.
View full definitionIsola's low-loss high-Tg FR-4 variant with improved signal integrity over standard 370HR.
View full definitionTesting an assembled PCB by powering it and verifying it performs its intended function.
View full definitionCoplanar waveguide with additional ground plane on opposite side of substrate.
View full definitionStandard file format for PCB manufacturing data, describing copper layers, solder mask, and silkscreen.
View full definitionSpecification of fiberglass weave pattern and weight used in laminate reinforcement.
View full definitionContinuous copper layer providing current return path and reference for signals.
View full definitionPCB materials without chlorine, bromine, and other halogenated flame retardants.
View full definitionSurface finish where boards are dipped in molten solder then leveled with hot air knives.
View full definitionRoHS-compliant HASL finish using lead-free solder alloys instead of traditional tin-lead.
View full definitionPCB technology using micro-vias and fine lines to achieve higher wiring density.
View full definitionMaterials with dielectric constant significantly above FR-4, used for size reduction or embedded capacitance.
View full definitionSignal frequencies or edge rates where transmission line effects and signal integrity matter.
View full definitionLaminate with elevated glass transition temperature for lead-free assembly and thermal stress.
View full definitionUltra-smooth copper foil with <2 µm surface roughness for high-speed signal integrity.
View full definitionRogers' thermoset laminate combining ceramic filler with woven glass, balancing RF performance and processability.
View full definitionIsola's workhorse low-loss laminate for high-speed digital designs up to 56 Gbps.
View full definitionAutomotive industry quality standard with requirements for defect prevention and supply chain traceability.
View full definitionElectrical test using a bed-of-nails fixture to verify component presence and values.
View full definitionThin gold layer deposited by chemical displacement reaction, used in surface finishes.
View full definitionOpposition to alternating current flow, measured in ohms, critical for high-speed signal integrity.
View full definitionManufacturing to specified characteristic impedance, typically ±10% tolerance.
View full definitionSignal power lost as it travels through a PCB transmission line.
View full definitionGlobal trade association that develops standards for electronics manufacturing.
View full definitionQuality and reliability classification system for PCBs (Class 1, 2, or 3).
View full definitionIPC standard classification for dedicated service electronic products.
View full definitionIPC standard classification for high-reliability electronic products.
View full definitionFoundational PCB design standard covering conductor spacing, trace width, via structures, and thermal management.
View full definitionDesign standard for flexible and rigid-flex PCBs, covering bend radius, pad placement, and stiffener design.
View full definitionDesign standard for HDI boards with microvias, fine lines, and high-density interconnects.
View full definitionXML-based data format that consolidates all PCB manufacturing data into a single intelligent file.
View full definitionSpecification for PCB base materials with 70+ slash sheets defining laminate properties.
View full definitionQualification and performance specification for rigid PCB fabrication, covering quality requirements by class.
View full definitionQualification and performance specification for flexible and rigid-flex PCBs.
View full definitionQualification specification for high-frequency PCBs used in RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave applications.
View full definitionComprehensive procedural guide for reworking and repairing PCB assemblies.
View full definitionVisual acceptance standard for bare PCB quality with photographs of target, acceptable, and nonconforming conditions.
View full definitionThe electronics industry's most widely used inspection standard for assembled PCBs and solder joints.
View full definitionData format standard for transmitting bare board electrical test information.
View full definitionQuality management standard specifically for medical device supply chains with strict traceability requirements.
View full definitionEnvironmental management certification for proper handling of chemicals, wastewater, and energy.
View full definitionFundamental quality management certification ensuring consistent processes and continuous improvement.
View full definitionMajor PCB laminate manufacturer known for FR-4 and high-speed materials.
View full definitionTaiwanese laminate manufacturer with strong high-speed and halogen-free product lines.
View full definitionGlobal standard for soldering materials, methods, and acceptance criteria in electronics assembly.
View full definitionDuPont's polyimide film brand, the standard base material for flex circuits.
View full definitionHong Kong-based manufacturer and the world's largest producer of copper-clad laminates.
View full definitionCured copper-clad material forming the rigid base layers of a PCB.
View full definitionBonding PCB layers together with heat and pressure to form a solid multilayer structure.
View full definitionUsing focused laser energy to create micro-vias in PCB layers.
View full definitionNumber of copper layers in a multilayer PCB.
View full definitionSoldering materials and processes without lead, required for RoHS compliance.
View full definitionRatio of energy lost to energy stored in a dielectric, equals dissipation factor.
View full definitionPackage or substrate containing multiple integrated circuits in a single unit.
View full definitionPanasonic's high-speed laminate series, the industry standard for 10-112 Gbps digital applications.
View full definitionPCB with metal base (aluminum or copper) for superior thermal dissipation.
View full definitionLaser-drilled via ≤150 µm diameter, typically connecting adjacent layers in HDI PCBs.
View full definitionCross-sectional sample of PCB features for quality inspection and analysis.
View full definitionTransmission line with a trace on the outer layer referenced to a ground plane below.
View full definitionRF signals from ~300 MHz to ~300 GHz, requiring specialized PCB materials.
View full definitionCurrent DoD performance specification for military PCBs with Qualified Manufacturers List program.
View full definitionLegacy military specification for rigid PCBs, still required for some existing military programs.
View full definitionPCB with three or more copper layers bonded together with dielectric.
View full definitionDrilled hole without copper plating, used for mounting hardware or component clearance.
View full definitionIntelligent CAD-to-CAM data format containing complete PCB manufacturing information.
View full definitionImpedance seen by each trace in a differential pair when driven differentially.
View full definitionTrace between two reference planes but closer to one than the other.
View full definitionResistive foil material for creating embedded resistors in PCBs.
View full definitionWater-based organic coating that protects copper from oxidation until soldering.
View full definitionCopper area for component attachment or via connection.
View full definitionFrame of waste material around a PCB panel that holds boards together during manufacturing.
View full definitionArranging multiple PCBs on a larger panel for efficient manufacturing.
View full definitionBoard with conductive traces that mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components.
View full definitionComplete system delivering power from supply to ICs, including planes and decoupling.
View full definitionAutomated machine that places surface-mount components onto PCB pads.
View full definitionCenter-to-center spacing between adjacent component leads or pads.
View full definitionTransformer using PCB windings instead of wound wire, enabling low-profile designs.
View full definitionElectrochemical deposition of copper or other metals onto PCB surfaces and hole walls.
View full definitionHigh-temperature polymer used as flexible PCB substrate and high-reliability rigid laminate.
View full definitionDedicated copper layer for power distribution to components.
View full definitionPre-impregnated fiberglass cloth that bonds layers together during lamination.
View full definitionLow-loss fluoropolymer material used in RF and microwave PCBs, commonly known as Teflon.
View full definitionDrilled hole with copper plating providing electrical connection between layers.
View full definitionAlternative term for PCB, emphasizing the wiring interconnect function.
View full definitionDuPont's dominant flex circuit material family based on Kapton polyimide.
View full definitionLeadless surface-mount package with contacts on the bottom and exposed thermal pad.
View full definitionSurface-mount IC package with leads extending from all four sides.
View full definitionPropagation mode where fields are approximately but not purely transverse.
View full definitionCopper foil pre-coated with resin, used for HDI build-up layers.
View full definitionEU chemical regulation with 200+ restricted substances, broader scope than RoHS.
View full definitionSignal energy bouncing back from impedance discontinuities in a transmission line.
View full definitionSoldering process where paste is melted in an oven to attach SMT components.
View full definitionHeated chamber that melts solder paste to form permanent solder joints.
View full definitionAssembly process where solder paste melts in an oven to attach surface-mount components.
View full definitionThe probability that a PCB performs its intended function over its design lifetime.
View full definitionZone of pure resin between tightly-spaced traces formed during lamination.
View full definitionEquipment for removing and replacing surface-mount components after initial assembly.
View full definitionElectromagnetic signals from ~3 kHz to ~300 GHz, requiring special PCB design considerations.
View full definitionTaconic's ceramic-filled PTFE laminate that processes like FR-4 for commercial microwave.
View full definitionWireless technology using electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects.
View full definitionPCB combining rigid board sections with flexible interconnect regions.
View full definitionRogers ceramic-filled PTFE laminate optimized for 77 GHz automotive radar.
View full definitionRogers hydrocarbon ceramic laminate that processes like FR-4 for RF applications to 10 GHz.
View full definitionRogers' most widely used RF laminate, the industry standard from 1 GHz to 77 GHz.
View full definitionMajor manufacturer of high-frequency PCB laminates, especially PTFE-based materials.
View full definitionEU directive restricting lead, mercury, cadmium, and other hazardous materials in electronics.
View full definitionThe process of defining copper trace paths connecting component pins.
View full definitionRogers' gold-standard PTFE laminate with the lowest loss for aerospace and satellite applications.
View full definitionMachine that applies solder paste to PCB pads through a stencil.
View full definitionAutomated soldering process for through-hole components on boards with SMT on the opposite side.
View full definitionMultiple lamination cycles used to create buried vias and HDI structures.
View full definitionResistance of a thin film measured in ohms per square, independent of square size.
View full definitionMajor Chinese laminate manufacturer offering FR-4 through high-speed materials.
View full definitionConductive enclosure or layer blocking electromagnetic interference.
View full definitionQuality of electrical signals, ensuring they arrive at receivers in usable condition.
View full definitionPrinted legend layer showing component designators, logos, and assembly markings.
View full definitionComponent designed to mount directly on the PCB surface without through-hole leads.
View full definitionPCB construction where solder mask is applied directly over copper without a surface finish underneath.
View full definitionAssembly method using automated placement of components on PCB surface pads.
View full definitionUnintended solder connection between adjacent pads or traces.
View full definitionThe metallurgical bond connecting a component lead to a PCB pad.
View full definitionProtective coating over copper traces, leaving pads exposed for soldering.
View full definitionMixture of powdered solder and flux used for SMT reflow assembly.
View full definitionThe ability of a surface to be wetted by molten solder, essential for reliable joints.
View full definitionMinimum distance between copper features, determined by voltage and manufacturing capability.
View full definitionAutomated inspection of solder paste deposits before component placement.
View full definitionFlattened fiberglass weave providing more uniform dielectric constant.
View full definitionMicro-vias placed directly on top of each other through multiple layers.
View full definitionThe arrangement of copper layers, cores, and prepregs defining a PCB's structure.
View full definitionMicro-vias offset from each other on successive layers to reduce filling requirements.
View full definitionThin metal sheet with apertures used to deposit solder paste onto PCB pads.
View full definitionTransmission line with a trace on an inner layer sandwiched between two ground planes.
View full definitionProtective coating applied to exposed copper to prevent oxidation and ensure solderability.
View full definitionTrace on outer PCB layer with ground plane below and air above.
View full definitionTrace centered exactly between two parallel ground planes.
View full definitionIsola's ultra-low-loss laminate for 100 Gbps+ applications with performance stable to 100 GHz.
View full definitionManufacturer of high-frequency PCB laminates, particularly PTFE-based materials.
View full definitionChange in resistance per degree of temperature change, expressed in ppm/°C.
View full definitionTemperature at which PCB laminate begins to chemically break down.
View full definitionMeasurement technique for verifying controlled impedance by analyzing pulse reflections.
View full definitionGradual widening of a trace where it meets a pad or via to improve reliability.
View full definitionPropagation mode where electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to direction of travel.
View full definitionImpedance-matching component at transmission line end to absorb signal and prevent reflections.
View full definitionSample structures on PCB panels for measuring impedance, plating thickness, and quality parameters.
View full definitionCustom hardware interface that connects test equipment to a PCB for automated testing.
View full definitionTemperature at which a laminate transitions from rigid to soft, affecting thermal reliability.
View full definitionMaterial's ability to conduct heat, measured in W/m·K.
View full definitionRepeated temperature fluctuations that stress PCB materials and solder joints over time.
View full definitionDesign techniques and materials for controlling heat in electronic assemblies.
View full definitionTime-temperature curve for reflow soldering, optimized for solder paste and components.
View full definitionSpoke pattern connecting a pad to a copper plane, balancing electrical connection with solderability.
View full definitionVia designed to conduct heat from a component to inner planes or the opposite board surface.
View full definitionComponent attachment using leads inserted through holes and soldered on the opposite side.
View full definitionTaconic's lowest-loss PTFE laminate for commercial satellite and radar applications.
View full definitionRogers ceramic-hydrocarbon thermoset series with Dk options from 3.27 to 12.85.
View full definitionAssembly defect where a component stands on end due to unbalanced solder forces.
View full definitionFixtures, stencils, and equipment setup required for PCB fabrication and assembly.
View full definitionCopper conductor on a PCB that carries electrical signals or power between components.
View full definitionThe width of a copper conductor, determining current capacity and impedance.
View full definitionControlled-impedance trace where signal wavelength is significant relative to trace length.
View full definitionSafety certification organization that tests and certifies PCB flammability and safety.
View full definitionUL safety standard for rigid and flexible PCBs covering flammability, thermal endurance, and electrical insulation.
View full definitionFlammability classification for plastics, where V-0 is the standard for FR-4 PCB materials.
View full definitionEpoxy material dispensed under BGAs and flip chips to improve thermal cycling reliability.
View full definitionHigh-energy light used in PCB manufacturing for imaging, curing, and inspection.
View full definitionPartial-depth cuts on PCB panels that allow boards to be snapped apart.
View full definitionUK/Asia laminate manufacturer known for thermal management and halogen-free materials.
View full definitionPlated hole connecting traces between PCB layers.
View full definitionCompletely filling vias with conductive or non-conductive material.
View full definitionFilling vias with non-conductive epoxy to seal and planarize the surface.
View full definitionUnused portion of through-hole via extending past the signal layer.
View full definitionCovering vias with solder mask to protect from solder and contamination.
View full definitionVia placed directly in a component pad, typically filled and planarized for SMD soldering.
View full definitionVia placed in SMT pad, filled and plated flat for component mounting.
View full definitionEffective ground reference formed equidistant between differentially-driven traces.
View full definitionAssembly process where PCBs pass over a wave of molten solder for through-hole components.
View full definitionEU directive for collection, recycling, and disposal of end-of-life electronics.
View full definitionNon-destructive inspection using X-rays to view hidden solder joints under BGAs and QFNs.
View full definitionThermal expansion perpendicular to the PCB surface, critical for via reliability.
View full definitionNo terms found matching your search.
Our engineers can help you navigate the complexities of PCB design and manufacturing. Get expert guidance on materials, stackups, and manufacturing processes.
Get a Quote